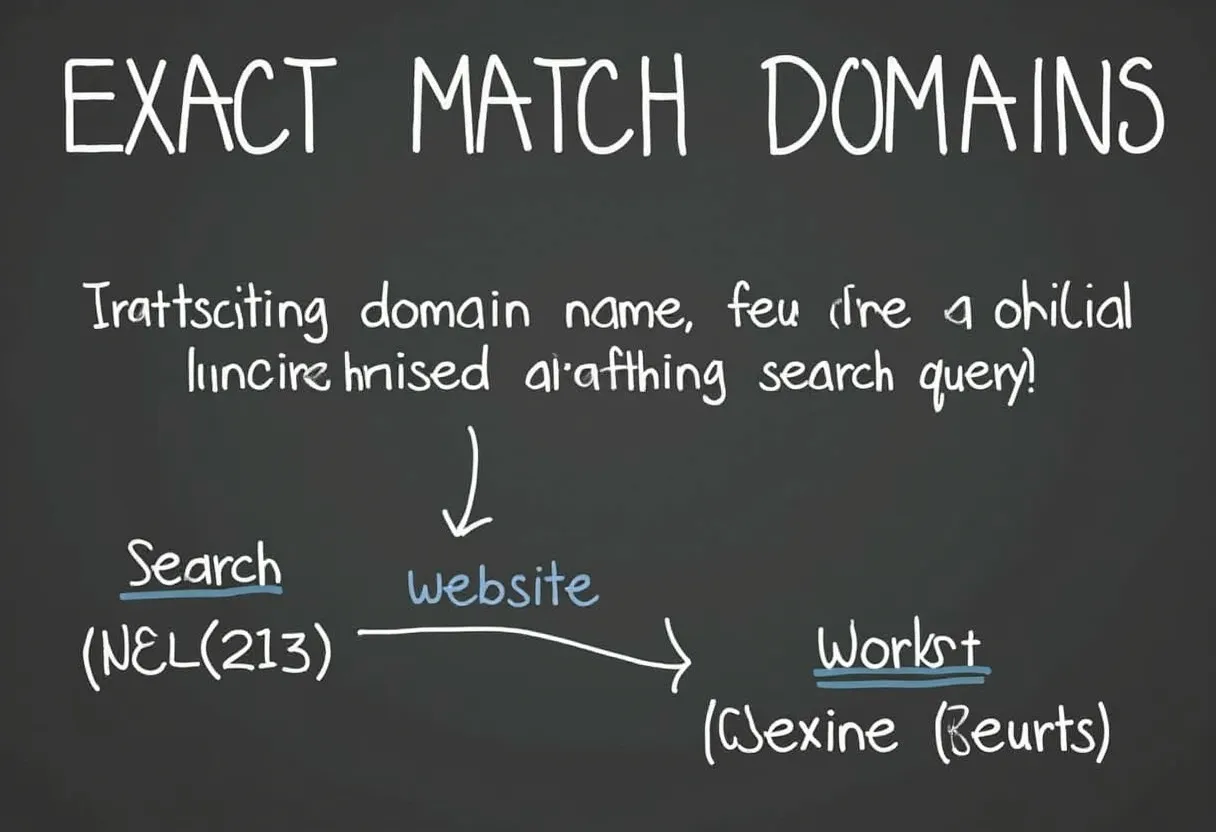
Exact Match Domains (EMD) in SEO
Definition
What are Exact Match Domains (EMD)?
Exact Match Domains (EMDs) are domain names that precisely match the exact keywords or phrase a website is trying to rank for in search engines. For example, if a website aims to rank for the search phrase “Boston injury lawyer,” an EMD would be BostonInjuryLawyer.com.
How It Works
Function and Concept of EMDs:
EMDs are designed to align closely with the search queries they target, making it easier for search engines and users to understand the website’s subject matter. Historically, EMDs tended to rank well because they directly matched the search query, providing a clear signal of relevance.
Relevance and User Intent:
EMDs help search engines understand the user intent behind the search query. For instance, a domain like hotels.com clearly indicates that the website is about hotels, aligning with the user’s search intent.
Backlink Profile and Branding:
EMDs can facilitate the creation of a topically relevant backlink profile. When a domain matches the target keywords, it is more likely to attract links with contextually relevant anchor text, which can enhance SEO efforts.
Content and Optimization:
While having an EMD is beneficial, it is crucial to pair it with high-quality content, good user experience, and a strong SEO effort to achieve and maintain good rankings.
Why It Matters
Importance of EMDs in SEO:
Ranking Advantage:
EMDs can provide a ranking advantage, especially for local search terms. They signal to search engines that the website is highly relevant to the search query, which can improve its position in search engine results pages (SERPs).
Credibility and Trust:
EMDs can generate instant credibility and trust with users. When a domain name matches the search phrase, users are more likely to click on it, assuming the site is trustworthy and relevant.
Click-Through Rates (CTRs):
EMDs can improve CTRs because users are more likely to click on a domain that exactly matches their search query. Higher CTRs can indirectly positively impact SEO by signaling to search engines that the site is relevant and useful.
Historical Context:
Google’s algorithm updates in 2012 aimed to reduce the impact of low-quality EMDs, but high-quality EMDs still maintain their value in SEO strategies.
Best Practices
Recommended Methods and Strategies for Using EMDs:
Quality Over Quantity:
Ensure that the EMD is paired with high-quality content and a strong user experience. Low-quality content can negate the benefits of an EMD.
Active Optimization:
Regularly update content and engage in active linking efforts to improve and maintain rankings. Passive efforts may take longer to yield results.
Brand Considerations:
While EMDs can provide short-term SEO benefits, they may limit long-term brand expansion and development. Consider the long-term implications of choosing an EMD.
Availability and Cost:
Be prepared to invest time and money in finding and purchasing a good EMD, as many desirable domains are already taken or expensive.
Complementary SEO Efforts:
Use EMDs as part of a broader SEO strategy that includes other optimization techniques such as anchor text optimization, social media integration, and local SEO practices.
Additional Considerations
In addition to EMDs, there are several related terms and concepts that can enhance your understanding and strategy in SEO:
Domain Age SEO:
Domain age refers to how long a domain has been registered. Older domains can sometimes have an edge in SEO because they have had more time to accumulate backlinks and establish authority.
Domain Authority Stacking:
This is a link building strategy that involves creating a hierarchy of related, authoritative domains to funnel link equity towards a target site, enhancing its overall authority and ranking potential.
Domain Rating (DR):
DR is a metric used by some SEO tools to measure the strength of a website’s backlink profile on a logarithmic scale from 0 to 100. Higher DR can indicate a stronger, more authoritative domain.
Domain Rebranding:
Rebranding a domain involves changing the domain name to better align with new business goals or branding strategies. This can impact SEO, especially if the new domain does not have the same level of authority or relevance as the old one.
Domain Structure:
Domain structure refers to the arrangement of the different parts of a domain, including the subdomain, domain name, and top-level domain (TLD). A well-structured domain can enhance both user experience and SEO.
Exact Match Anchor Text Recovery:
Exact match anchor text involves backlinks with text that exactly matches the target keyword. Overuse can lead to penalties; thus, recovery includes diversifying anchor text and disavowing low-quality links.
Partial Match Domains (PMD):
If an exact match domain is not available, consider using partial match domains, which can still provide relevance signals and improve SEO rankings.
Top-Level Domain (TLD):
The TLD is the last part of a domain name, such as .com, .org, or .net. Choosing the right TLD can influence SEO, with some TLDs being more trusted or relevant than others.
Conclusion
Exact Match Domains (EMDs) can be a valuable asset in an SEO strategy, offering potential ranking advantages, credibility, and improved click-through rates. However, their success depends on pairing them with high-quality content, good user experience, and complementary SEO practices. With the right approach, EMDs can significantly enhance a website’s visibility and effectiveness in search engine results.